Globodera tabacum
Lownsbery & Lownsbery (1884)
Tobacco cyst nematodes
- synonyms : Globodera tabacum tabacum or Heterodera tabacum ; Globodera tabacum solanacearum, Globodera solanacearum ;Globodera tabacum virginiae, Globodera virginianae
Globodera tabacum species is composed of three subspecies: Globodera tabacum strict sense, Globodera solanacearum and Globodera virginiae.
Cyst nematodes are much less damaging on tobacco than Meloidogyne spp. and Pratylenchus. Their distribution is also more limited than the other two genus. They have been reported in some countries of the major continents, including China, Pakistan, the United States and several European countries such as Italy, and Greece .
 |
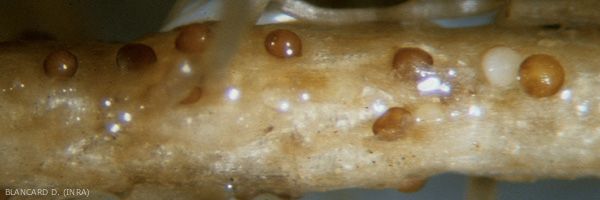
| Figure 1 |
In France, outbreaks on tobacco have mainly been observed in the Southwest, specifically in the Lot-et-Garonne region. Those outbreaks were reported on a few crops with large number of diseased plants that caused significant losses (figure 1). Only the sub-species Globodera tabacum sensu stricto was reported to be associated with those outbreaks.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
China situation
In China, tobacco cyst nematode was mainly observed in some areas of Henan and Shandong province. The distribution has expended in recent years. Cyst nematode species is Heterodera glycines which is different from Globodera tabacum. Preliminary studies showed that the pathogenicity of cyst nematode which infects soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) and tobacco greatly varied, and may belong to different biotype.
At adult stage, Heterodera glycines produces white or yellow cysts (females) on the roots (figure 3). The most damaged root branchings become brown and necrotic with reduced growth, and finally die. Black brown circles usually remain on dead root particles, they are cysts or small pits and after cysts fall off (figure 4). Symptoms for tobacco plants include slow growth, yellow leaves and tip curl down (figure 2).
Heterodera glycines bred four generations in one year on tobacco. Every generation develops 27 (22~35) days, but the fourth generation is incomplete. This disease usually appears late in May, the peak of incidence is in June-July, and infection weakens in August.
Many methods for managing Meloidogyne spp. can also be used to control Heterodera glycines. Moreover, it is advised not to rotate with soybean.
| Figure 2 | Figure 3 | Figure 4 |
(Jing Wang - Tobacco Research Institute, Chinese Agricultural Academy of Science, China)