Pyrenochaeta lycopersici R.W. Schneid. & Gerlach (1966)
Fungal corky root
- classification : Fungi, Ascomycota, Dothideomycetes, Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, Incertae sedis
- Distribution and damage
This fungus, responsible for the disease of the corky roots of tomatoes ("Corky root"), also colonizes those of lettuce. It has only been reported on the latter plant very rarely , mainly in England and France. Its impact on lettuce is only occasionally significant, resulting in a reduction in plant vigor and therefore in lettuce size at harvest.
- Symptoms
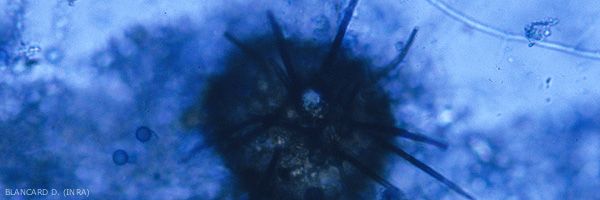
Pyrenochaeta lycopersici causes brown changes , superficially corky that surround the roots in the form of sleeves (Figures 1 and 2). These alterations can be found on the taproot and secondary roots. A number of rootlets disappear. Although it can be confused with the symptoms associated with the corky taproot, the damage caused by this fungus is never so significant. Despite everything, lettuces have a limited development and appear more or less puny. The pycnidia of this fungus are rarely seen on altered tissue (Figures 3 and 4).
- Elements of biology
It is preserved in the soil on plant debris. Several hosts cultivated rotating with lettuce are capable of harboring and multiplying it; this is the case for tomatoes, melons, eggplants, beans ... It is the same for several weeds. It penetrates the root tissues then gradually causes their suberization and rotting. Its dissemination takes place mainly through contaminated plants and / or substrates, tillage tools ... There seem to be at least 2 types of strains: “cold” strains with a thermal optimum between 15-20 ° C and “hot” strains still pathogenic at 30 ° C. The production of sensitive crops in the same plot favors its extension into the soil.
- Protection
This soil-borne fungus requires most of the control methods recommended to combat Sclerotinia spp . should be carried out Crop rotations excluding the susceptible plants reported. In some cases, disinfection of the soil with dazomet will be necessary ( e-phy ): favor solarization . Eliminate as many roots as possible at the end of the crop to reduce the amount of contaminated plant debris returning to the soil. Varietal sensitivity differences were observed.
NB: The legislation on pesticides evolving very quickly, we advise you to consult the e-phy site of the Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries which is an online catalog of plant protection products and their uses, fertilizers and culture media approved in France. This also applies to all biological products based on microorganisms or natural substances.