Trichothecium roseum (Pers.) Link, (1809)
(fruit rot)
Trichothecium roseum (Pers.) Link, (1809) * is a fungus widely distributed in the world and on many living and dead plants. It has been reported on various fruits (apple, pear, plum, cherry ) and vegetables (melon, cucumber ). It seems more confidential on tomatoes on which it has been reported in particular on fruits produced under shelter: in North Carolina, Czechoslovakia, Italy (Liguria), Japan. It has been observed very occasionally in France, also in glasshouses. It would also have been isolated from lesions caused by Phytophthora infestans .
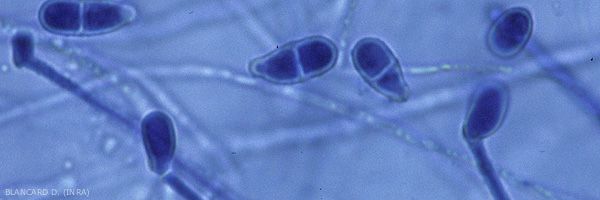
This fungus causes dark lesions, mottled with brown veins, which appear near the stalk scar of fruit (Figures 1). This, in addition to being surrounded by a brown area, is covered with a pale pink mold. This mold is made up of the long, arbuscular conidiophores of the fungus bearing bicellular, smooth and hyaline, elongated or pyriform conidia (Figures 2 and 3). Generally, affected fruits may drop prematurely. Trichothecium roseum can synthesize a mycotoxin in damaged tissue: trichothecene.
Generic protection methods are available at the following link .
* Anamorphe de Hypocreales.
Classification : Fungi, Ascomycota, Pezizomycotina, Sordariomycetes, Hypocreomycetidae, Hypocreales, Incertae sedis